Geography of Zambia
  | |
| Continent | Africa |
|---|---|
| Region | Southern Africa |
| Coordinates | 15°S 30°E / 15°S 30°ECoordinates: 15°S 30°E / 15°S 30°E |
| Area | Ranked 39th |
| • Total | 752,618 km2 (290,587 sq mi) |
| Coastline | 0 km (0 mi) |
| Borders | 5,664 km (Angola 1110 km, Democratic Republic of Congo 1930 km, Malawi 837 km, Mozambique 419 km, Namibia 233 km, Tanzania 338 km, Zimbabwe 797 km, Botswana <1 km) |
| Highest point | Mafinga Central, Mafinga Hills 2,339 m |
| Lowest point | Zambezi River, 329 m |
| Longest river | Zambezi River 2,650 km |
Zambia is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa, to the east of Angola. It has a total area of 752 618 square kilometres (slightly larger than France), of which 9 220 km² are water.
Political geography
Zambia has a total of 5 664 km of land boundaries, and it borders: Angola for 1 110 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo for 1 930 km, Malawi for 837 km, Mozambique for 419 km, Namibia for 233 km, Tanzania for 338 km, Zimbabwe for 797 km, and Botswana, less than 1 km (0.62 mi).
Physical geography
Climate
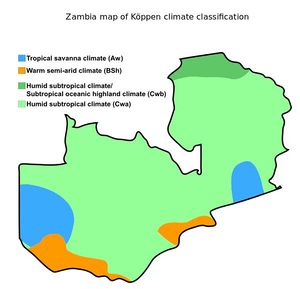
Zambia has a tropical climate, modified by the altitude of the country. There is a rainy season that runs from October/November to March/April and September.
Terrain
Template:MapLibrary The terrain of Zambia is mostly high plateau, with some hills and mountains. The lowest point is the Zambezi river, at 329 m (1,079 ft) above sea level, with the highest being Mafinga Central in the Mafinga Hills, at 2,339 m (7,674 ft) above sea level.
Ecoregions
Nine ecoregions in four biomes are represented in Zambia, the most widespread being Miombo, Mopane and Baikiaea woodland savanna, with grasslands (mainly flooded grassland) and evergreen forest also present.
Land use
The following table describes the land use in Zambia, as of 2011.
| Use | Percentage of Area |
|---|---|
| arable land | 4.52 |
| permanent crops | 0.05 |
| other | 95.44 |
As of 2005, 1559 km² of land in Zambia is irrigated.
Environment
Current issues for the environment in the country include: air pollution and resulting acid rain in the mineral extraction and refining region; chemical runoff into watersheds; poaching, which seriously threatens: rhinoceros, elephant, antelope, and large cat populations; deforestation; soil erosion; desertification and lack of adequate water treatment, which presents human health risks.
Zambia is party to the following international agreements: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection and Wetlands. Zambia has signed, but not ratified, the Kyoto Protocol
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of Zambia, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northernmost point - Cape Pungu, Northern province
- Easternmost point - Kongula Peak, Northern province
- Southernmost point - unnamed location on the border with Zimbabwe in the Zambezi River, Southern province
- Westernmost point - the western section of the border with Angola*
* Note: Zambia does not have a westernmost point as the border here is formed by the line of longitude 22° E